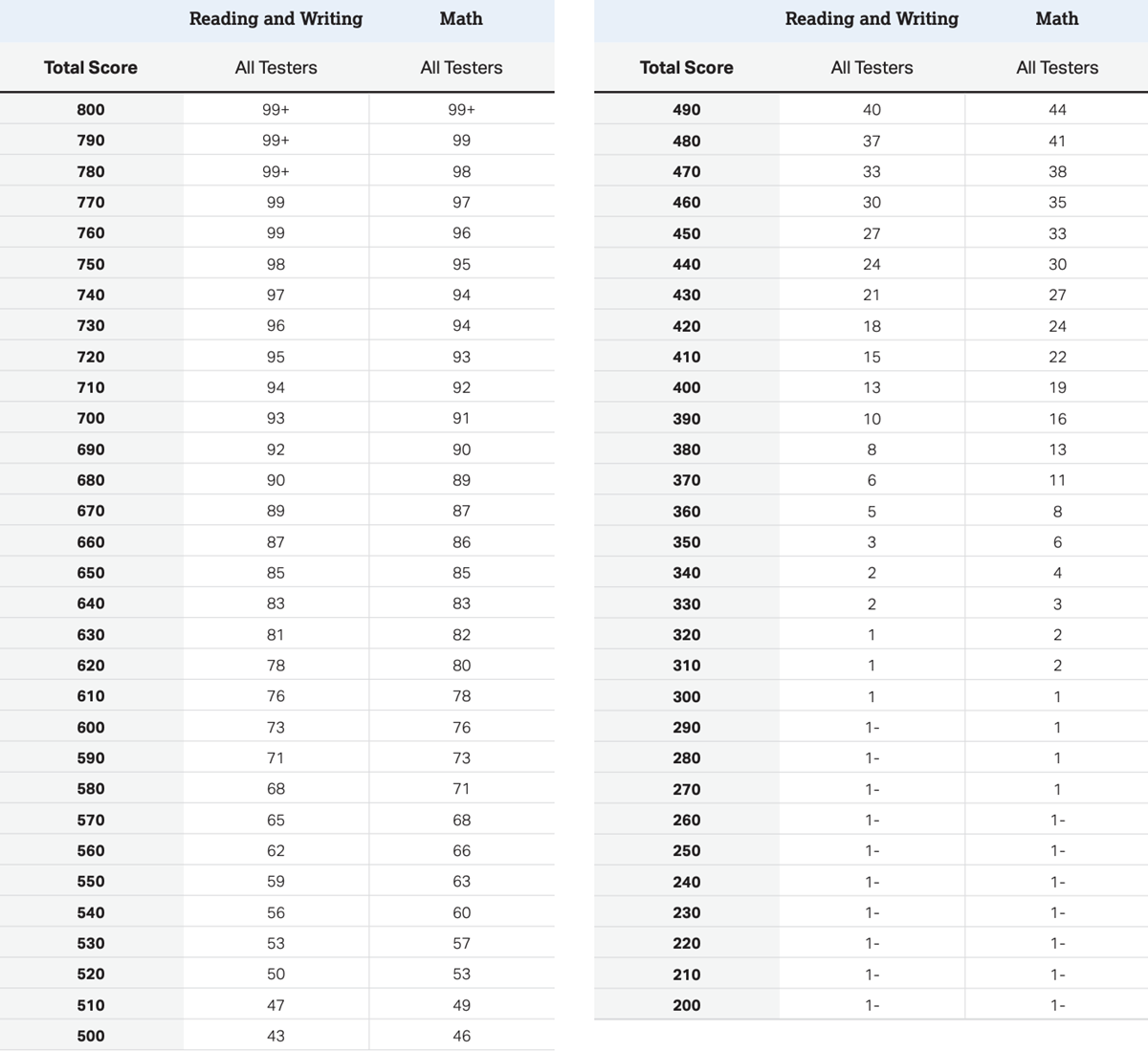
iReady Diagnostic Scores by Grade 2025 (2024-2025) Math + Reading
iReady Diagnostic Scores by Grade 2025 (2024-2025) Math + Reading:
Welcome to Schoolsnews.org: School News, iReady Diagnostic Scores by Grade Level 2025, NWEA Map Scores by Grade level 2025, SAT Scores 2025, Tests, High School Grades, and much more.
We have all the latest test scores charts for Elementary Schools, Middle Schoolers, High School and College students. Additionally, you are very welcome to browse our ‘Fun’ section, for amazing drawing ideas, funny riddles for kids, and much more.
Latest Articles.
Other Resources:
NWEA MAP Test Scores – NWEA Map Scores for 2024-2025.
MAP Scores by Grade Level 2025 – NWEA Map Scores by Grade Level 2024-2025.
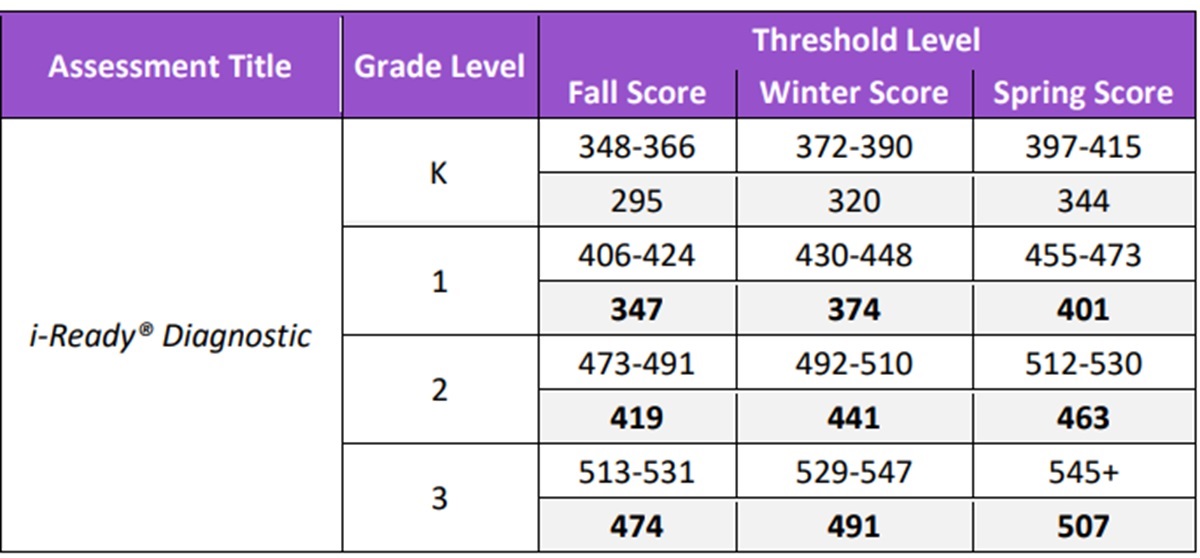
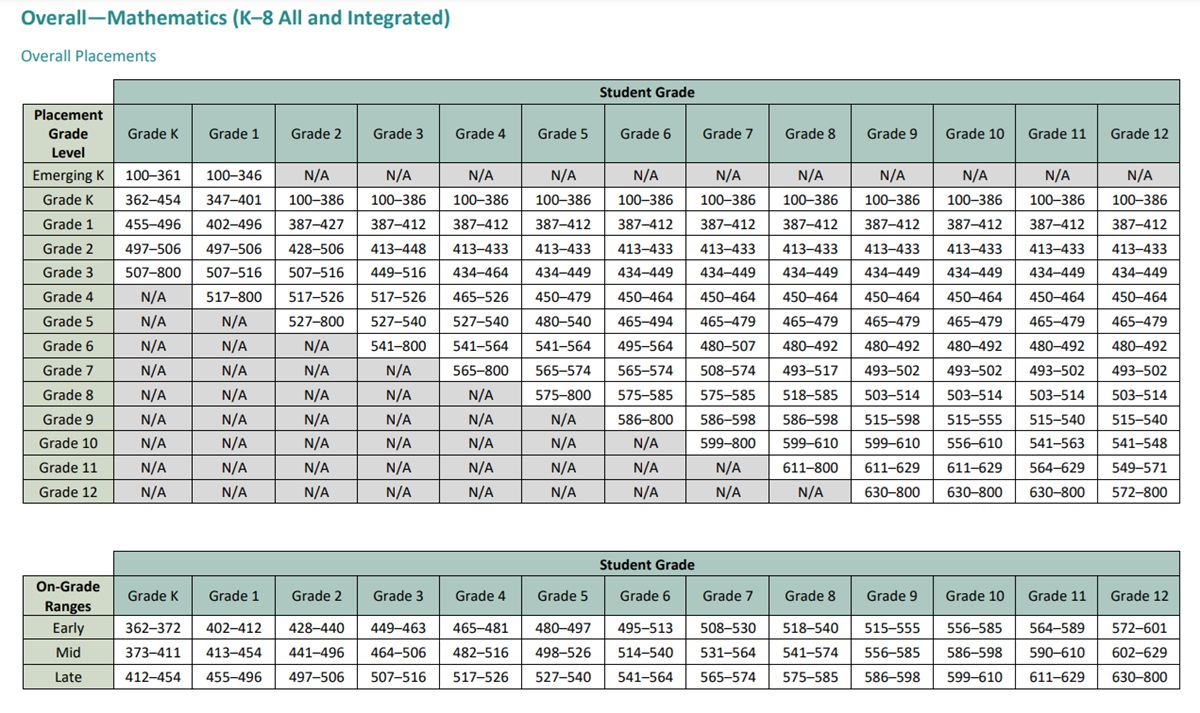
iReady Diagnostic Scores by Grade Level Math 2025 – iReady Diagnostic Scores for Math.
iReady Diagnostic Scores by Grade Level Reading 2025 – iReady Diagnostic Scores for Reading.
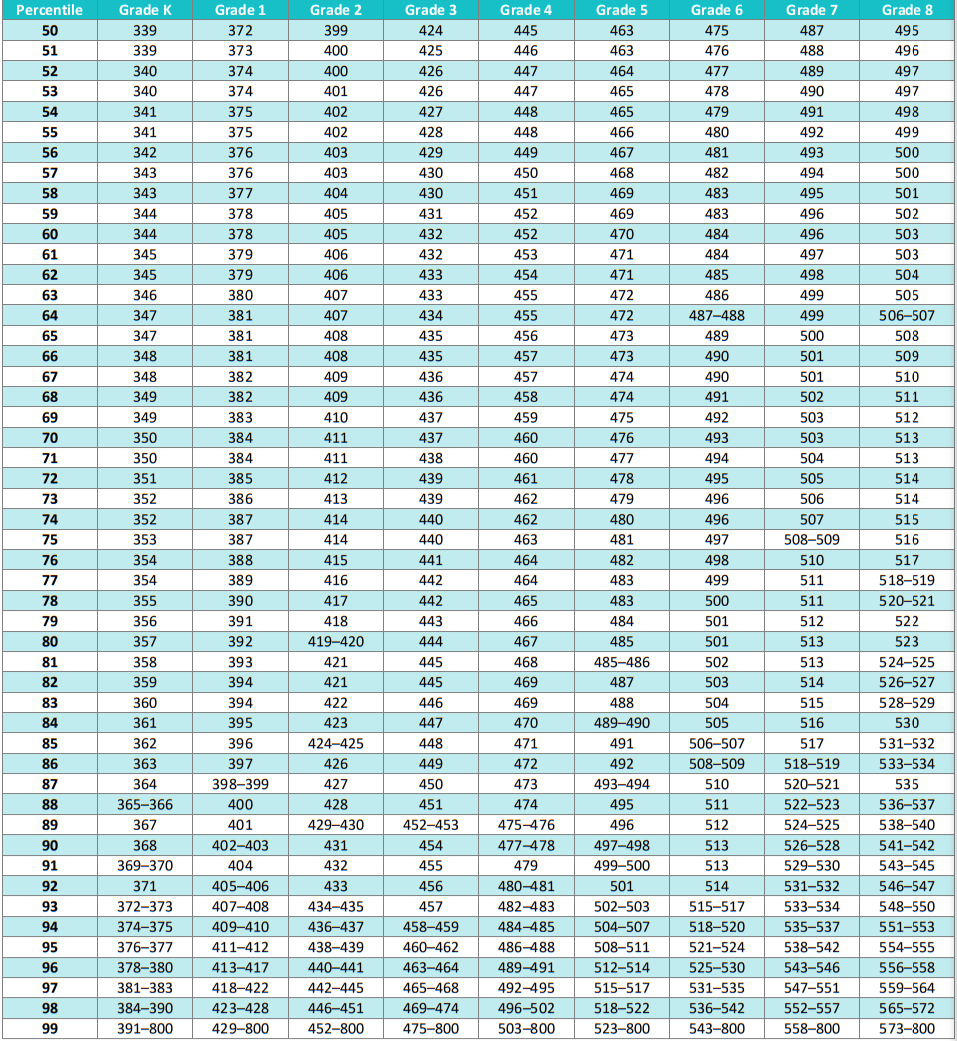
iReady Diagnostic Scores Percentiles by Grade Level Math 2025 – iReady Diagnostic Scores for Math.
iReady Diagnostic Scores by Grade Level Reading 2025 – iReady Diagnostic Scores for Reading.
What is Level Z in iReady
Reading Level Chart
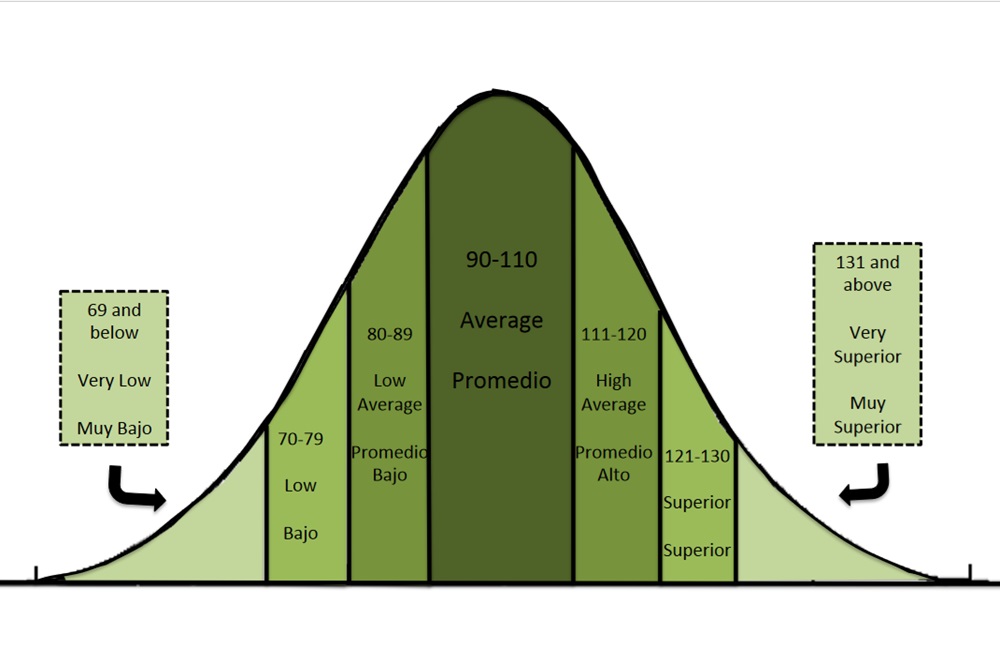
What is the average IQ for a 12 year old
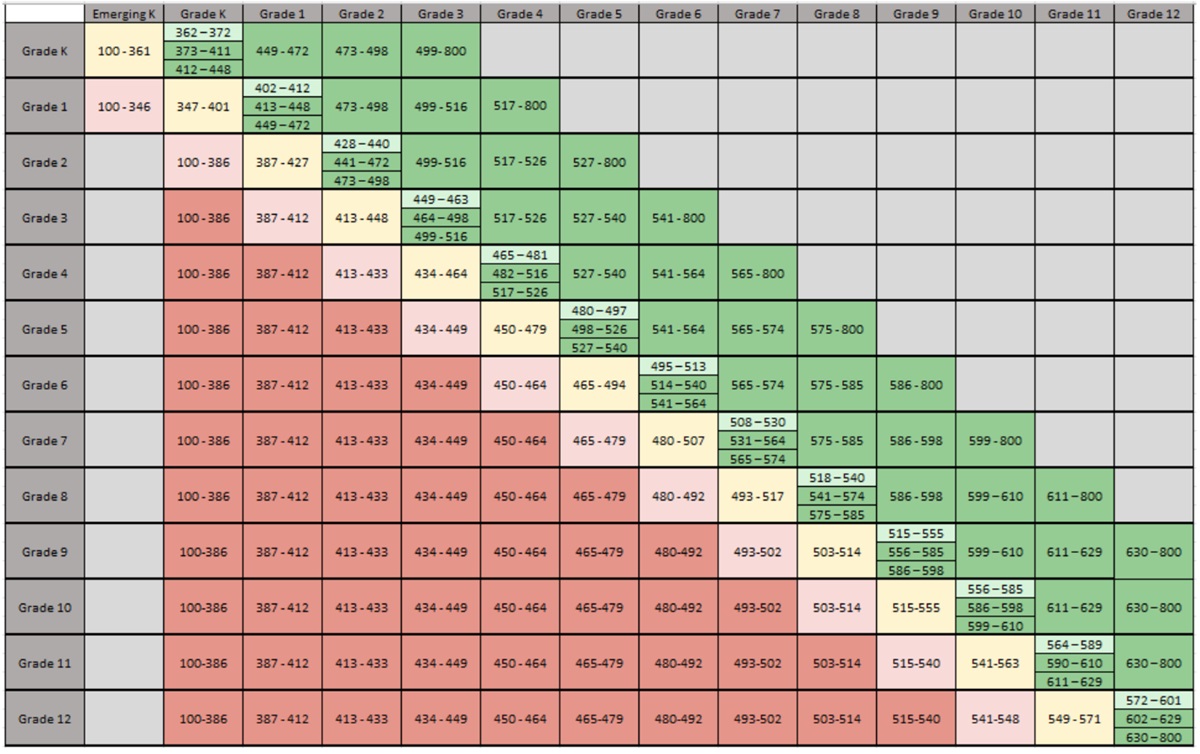
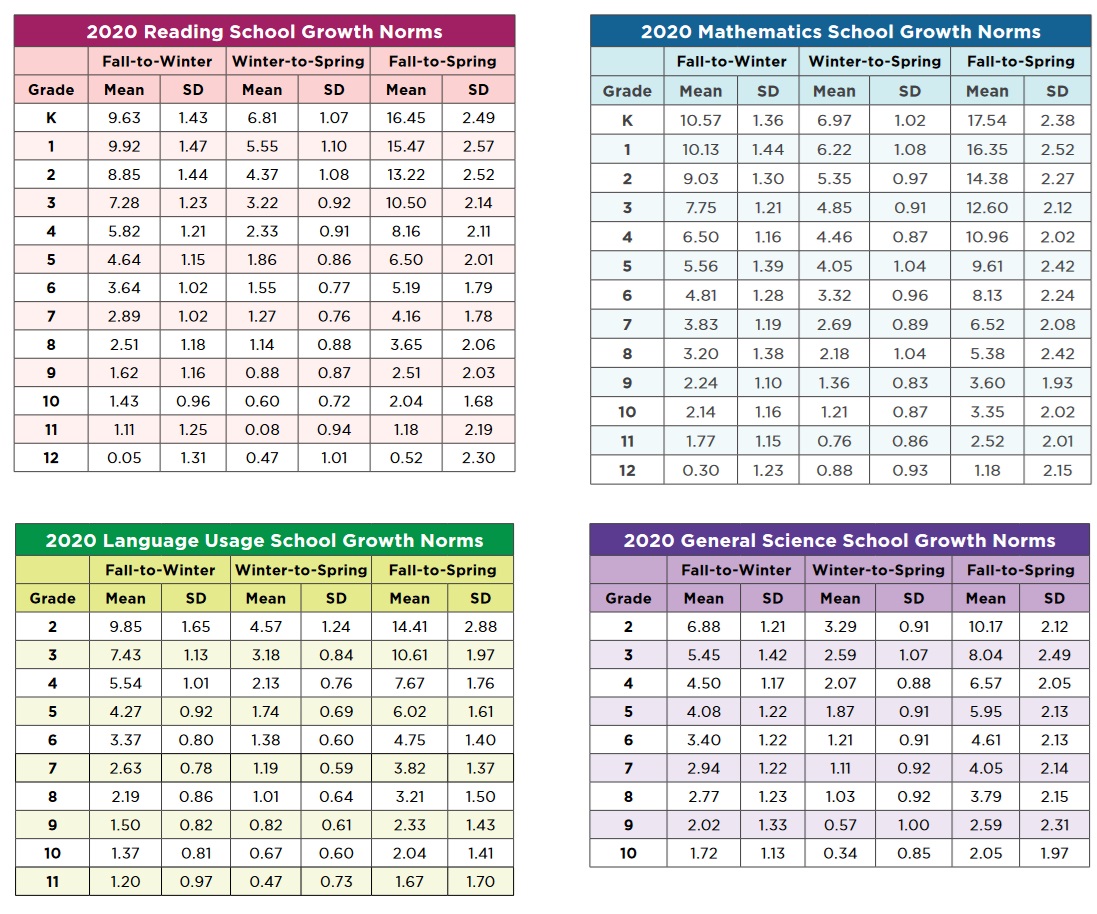
Map Scores by Grade Level PDF
What is a Good iReady Diagnostic Score for 8th Grade – What is a Good iReady Score – Guide.
What Grade is Level E in iReady? – i-Ready Levels by Grade.
www.Mcgift.giftcardmall.com – Mcgift.giftcardmall.com Activate. Mcgift.giftcardmall Home.
www.Mcgift,giftcardmall.com Mastercard.
www.Mygift.giftcardmall.com – www.giftcardmall.com/mygift Activate. Giftcardmall/mygift Home.
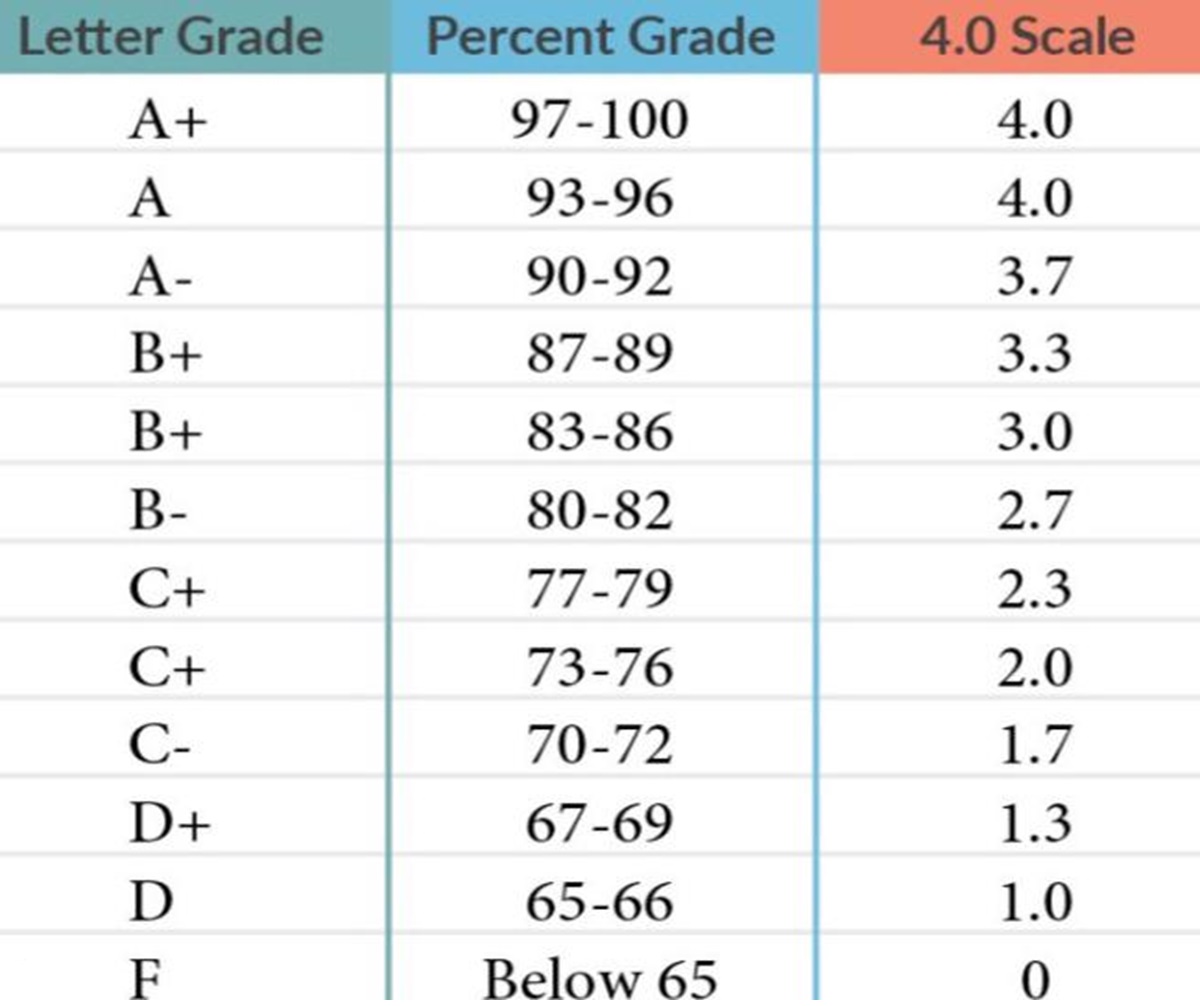
Grade calculator and Funny Dad Jokes.
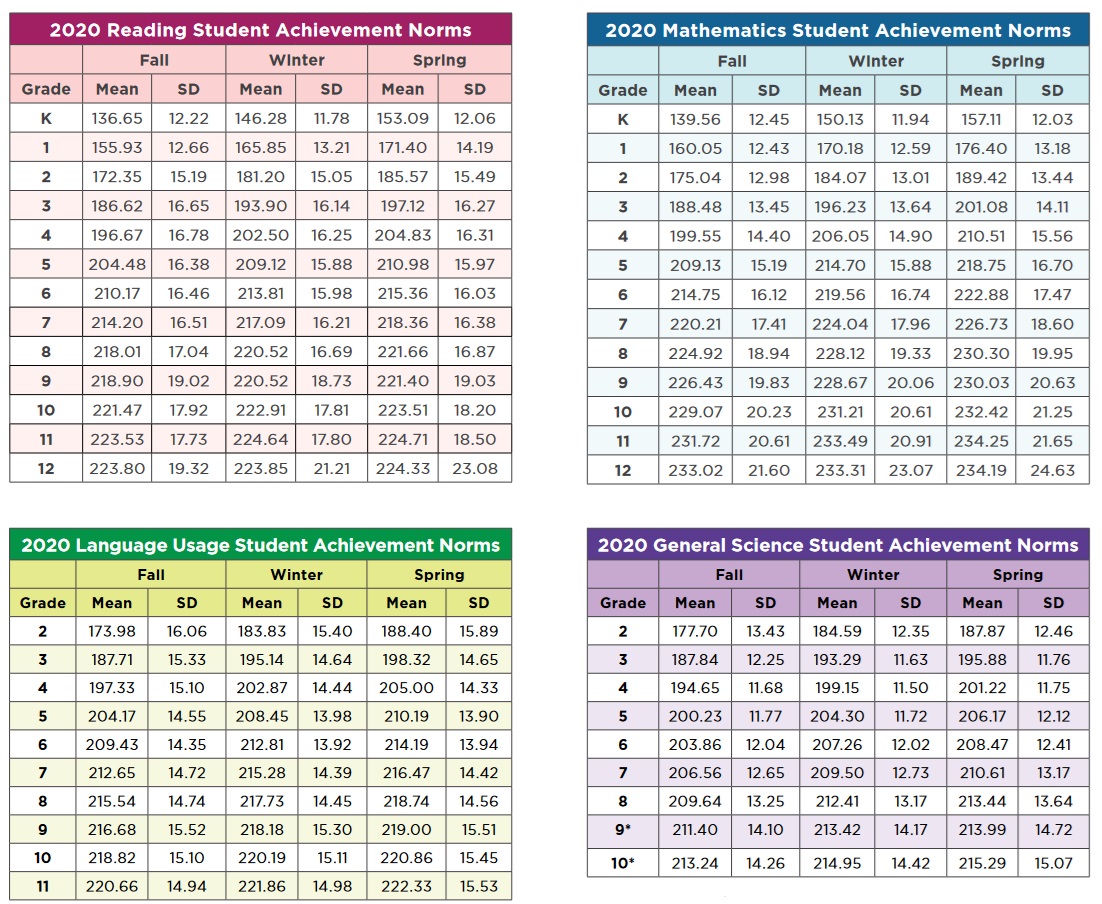
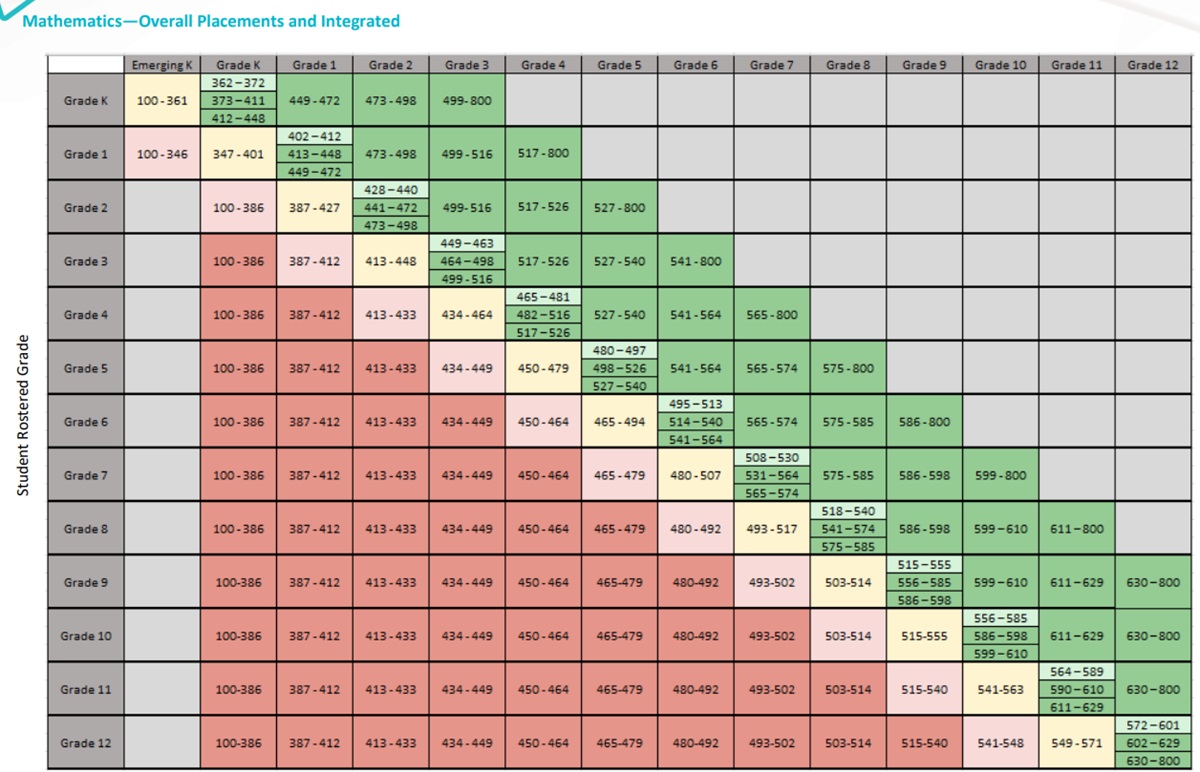
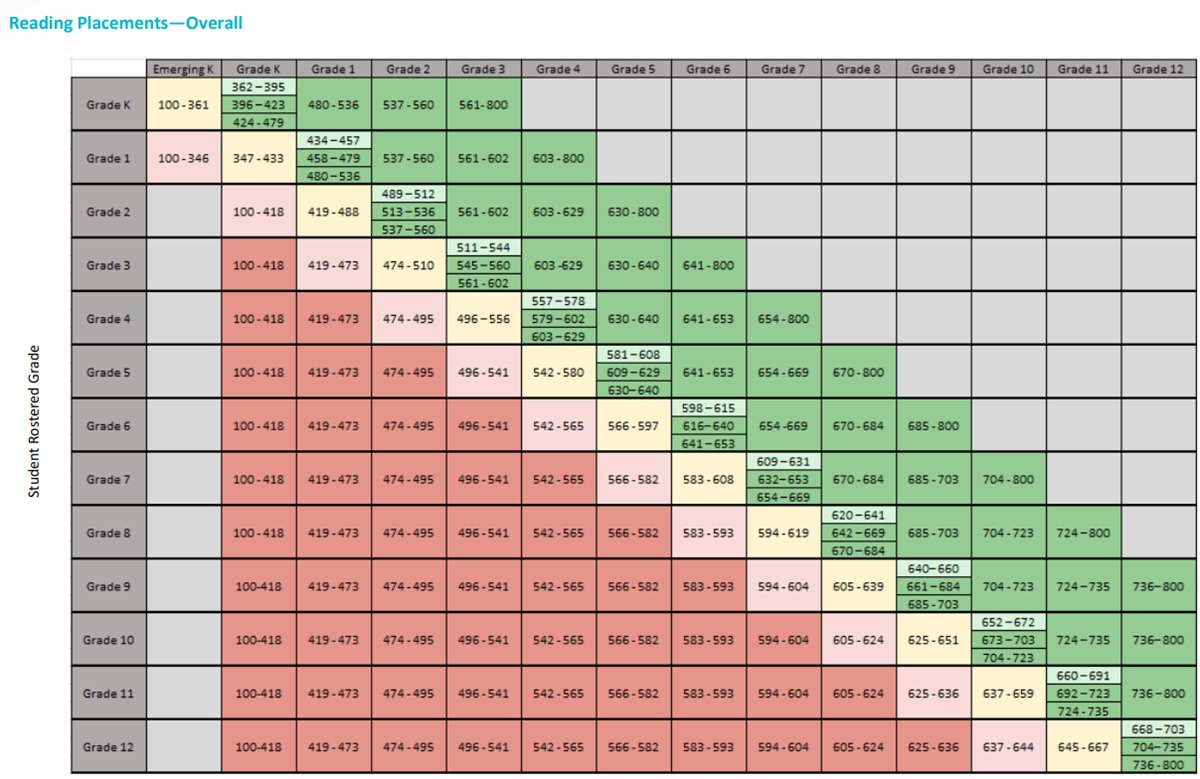
iReady Diagnostic Scores by Grade 2025 (2024) in Math + Reading
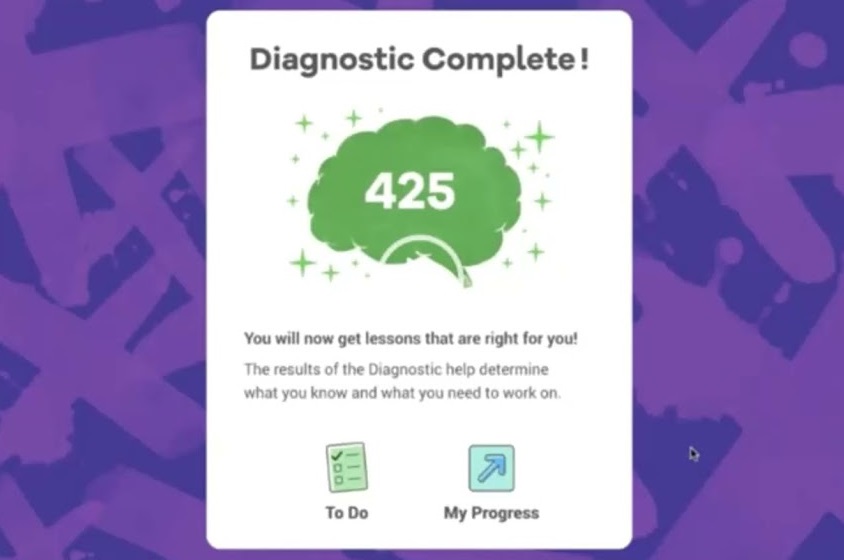
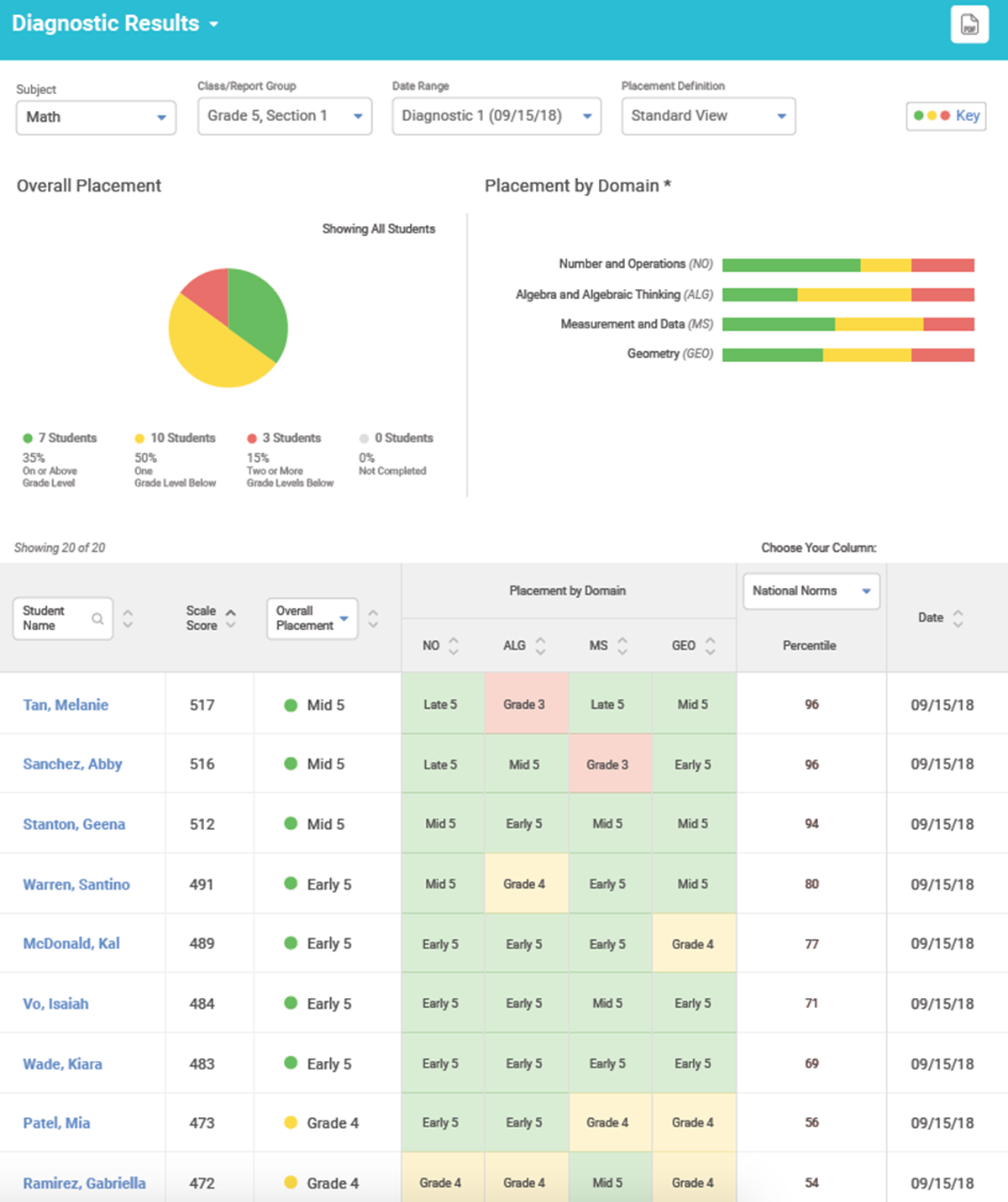
The i-Ready Diagnostic is an adaptive test used for grades K–8. It evaluates student progress in both math and reading by providing detailed scores that highlight strengths and areas for improvement. Teachers use these scores to tailor instruction and support each student’s learning journey throughout the year.
NWEA Map Test Scores by Grade Level 2025 (2024)
The NWEA MAP test is an adaptive assessment that measures academic growth in math and reading. It delivers RIT scores, allowing educators and parents to track a student’s progress over time and compare performance against national benchmarks. This data helps identify areas of success and opportunities for additional support.
Thank you for visiting!








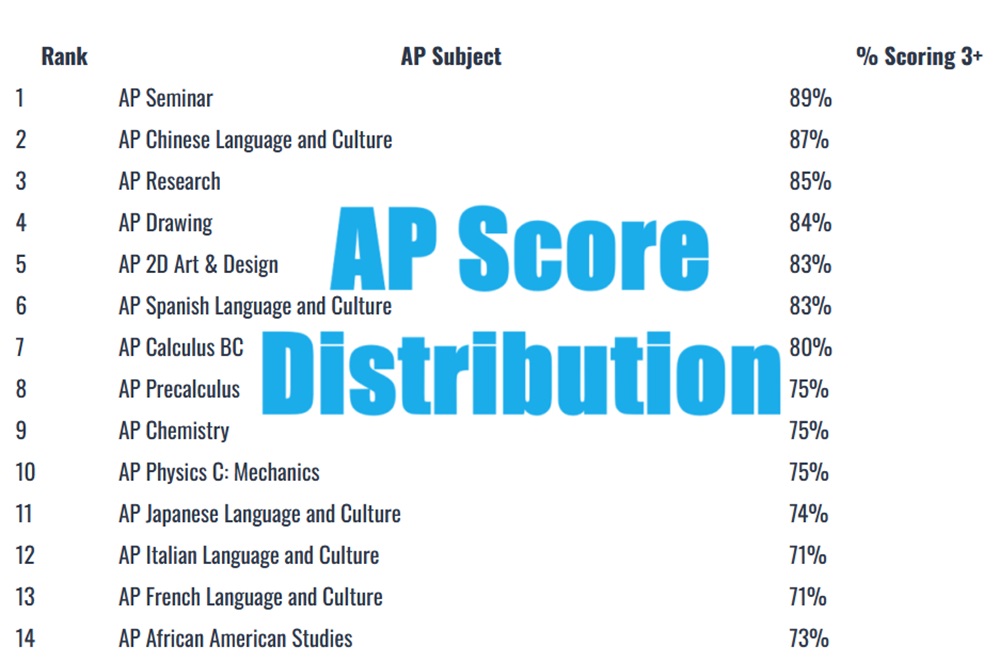

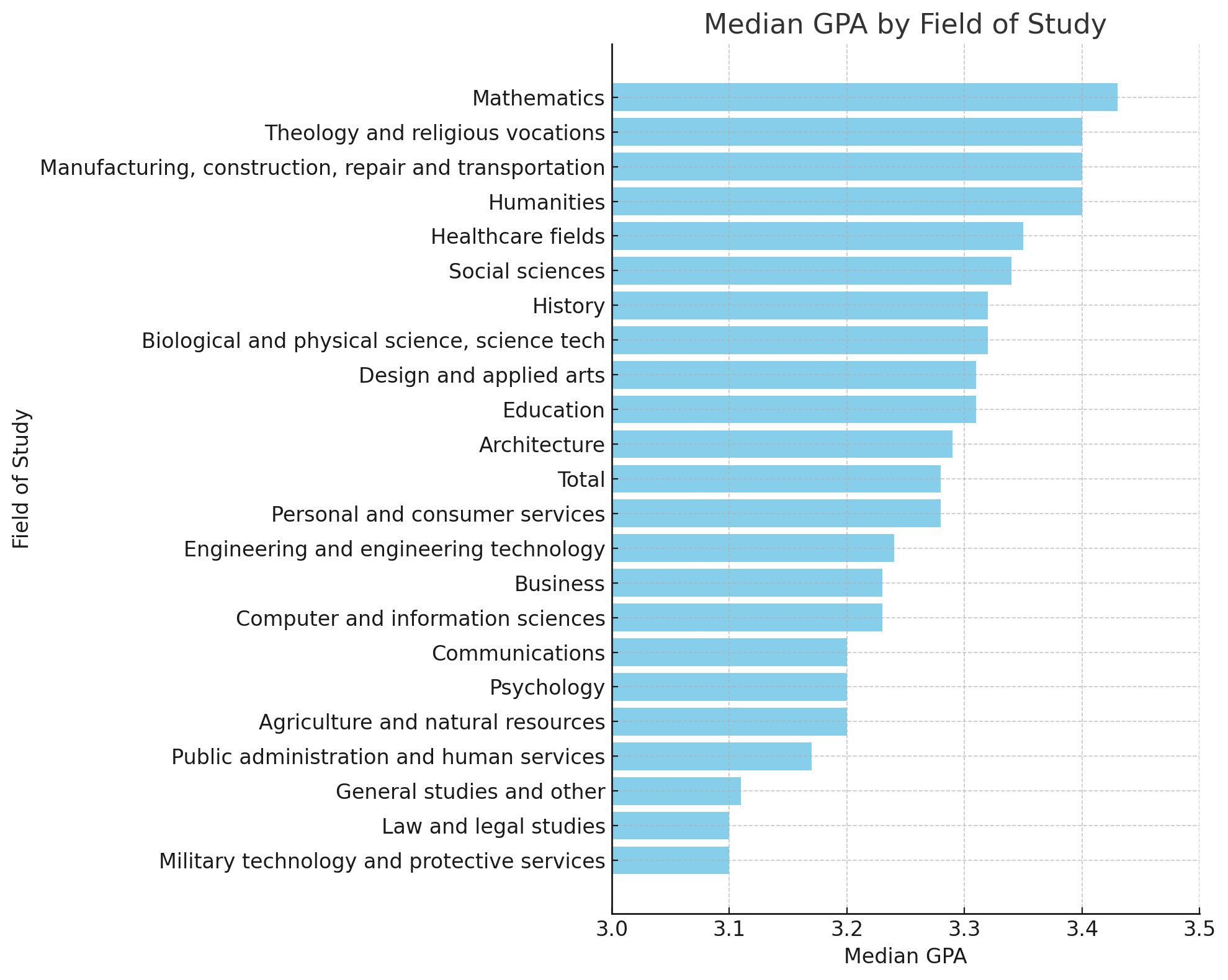
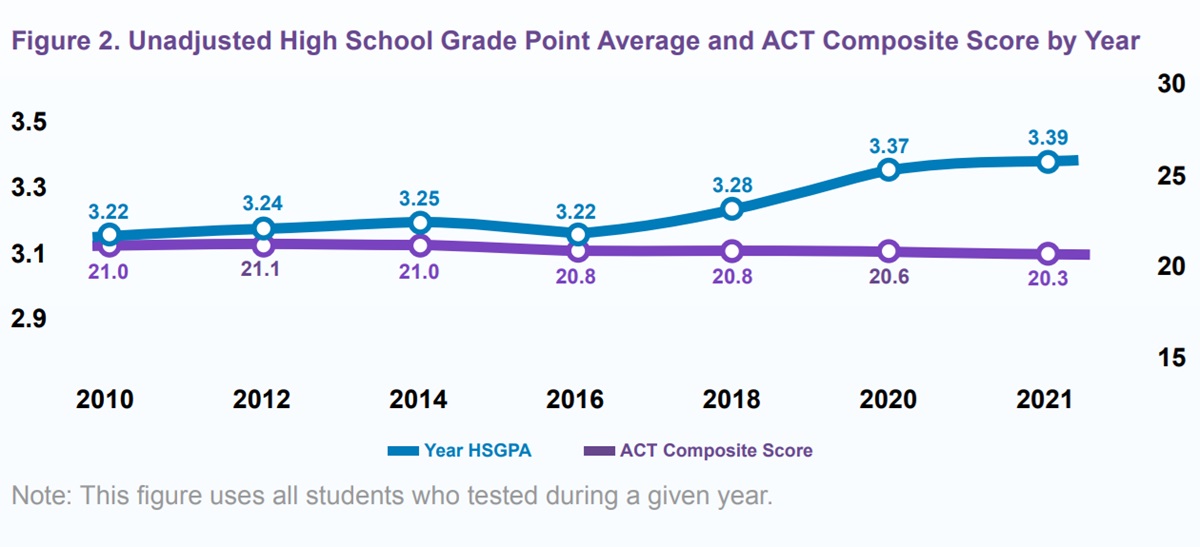
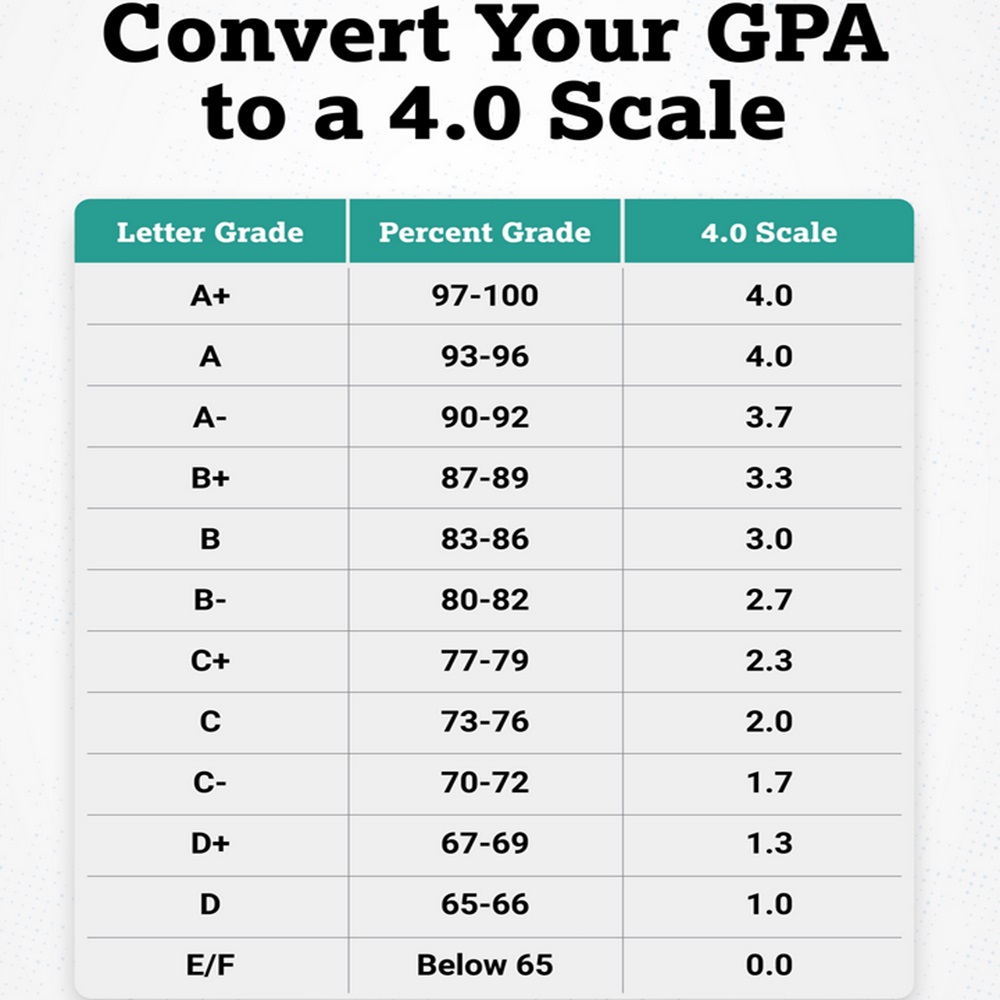







Ohio Asset Compass addressed lookback period concerns effectively.