High School Grades Levels · Elementary + High School Grade Charts & Ages
High School Grade Levels.
How many grades are there in High School? What are the different High School, Middle School and Elementary grade levels called? And, what does the U.S High School grades system look like? (A, B, C Letter grades vs percentage scores). Get the answers here.
U.S. Education Levels.
The U.S. education system includes several levels of public schooling that children must attend by law. These levels are divided into preschool, elementary school, middle school, and high school. If you’re new to the U.S. education system or need to learn how students are placed in grades, this guide will help you understand the different education stages.
In the United States, there are 12 grades after the first year of kindergarten. The main levels of education are:
- Preschool (Early Childhood Education) – 2-4 Years Old.
- Elementary School – 5-10 years Old.
- Middle School – 11-13 Years Old.
- High School – 14 to 18 years old.
1. Early Childhood Education (Preschool).
Early childhood education includes preschool and daycare, which are not required by law. This type of education is for children before they start kindergarten, often between ages 2 and 4.
- Daycare can begin just a few months after a baby is born.
- Preschool usually starts as early as age 2 or 3.
- Cost: Preschool and daycare typically require a fee, though low-income families might qualify for free preschool programs like “Head Start.”
- Purpose: Preschool helps children learn social skills and prepare for kindergarten.
2. Elementary School.
- Grades: Kindergarten (K) to Grade 5
- Ages: Typically 5 to 10 years old
- Structure: Students usually stay in the same classroom with one teacher for most subjects.
- Subjects: Reading, writing, math, critical thinking, and problem-solving.
Elementary school builds the foundation for core subjects like reading and math. Students start with kindergarten around age 5 and progress to grade 5 by age 10.
3. Middle School (Junior High).
- Grades: 6 to 8
- Ages: Typically 11 to 13 years old
- Structure: Students switch classes for different subjects and have multiple teachers.
- Subjects: English (grammar, reading comprehension), Math (fractions, percentages), Science (basic biology, chemistry), and Social Studies (civics, economics).
Middle school helps students transition from having one teacher to multiple teachers, and it starts building more complex skills.
4. High School.
- Grades: 9 to 12
- Ages: Typically 14 to 18 years old
- Structure: Classes are organized by subject, with different teachers throughout the day.
- Subjects: English (literature and essay writing), Math (algebra to calculus), Science (biology, chemistry, physics), and Social Studies (U.S. and world history).
High school is more advanced, and students can take specialized courses to prepare for college or specific careers. Students can also join clubs, sports, and extracurricular activities.
Grade Names in High School:
- 9th Grade: Freshman
- 10th Grade: Sophomore
- 11th Grade: Junior
- 12th Grade: Senior
Some students choose advanced classes like AP (Advanced Placement) or IB (International Baccalaureate) to earn college credits early.
How many Grade are There in High School?
In the United States, high school consists of four grades, which are:
- 9th Grade – Often called Freshman year (typically ages 14-15)
- 10th Grade – Often called Sophomore year (typically ages 15-16)
- 11th Grade – Often called Junior year (typically ages 16-17)
- 12th Grade – Often called Senior year (typically ages 17-18)
These four grades make up the high school education phase, from grade 9 to grade 12. Each grade level builds on the previous one, preparing students for graduation and either further education or entering the workforce.
Secondary School.
In some areas, students may attend a secondary school instead of a traditional high school. Secondary schools cover grades 9 to 12 and provide vocational training like carpentry or automotive technology.
Post-High School Education
After high school, students can pursue higher education at a college or university. Students need to apply to colleges, meet requirements, and pay tuition. There are scholarships and financial aid available to help pay for college.
Middle School and High School Class Placement.
In middle and high school, students may be placed in different levels of classes based on their abilities and needs. This is called “class placement.” Here are some of the ways schools determine class placement:
- English proficiency: If a student needs help with English, they may be placed in a class designed for English learners.
- Test Scores: Schools use standardized tests, such as i-Ready Math Tests or NWEA Map Tests, or other assessments to place students.
- Teacher or Counselor Recommendations: A teacher or counselor may recommend a specific class level.
- Parental Input: Parents can discuss their child’s learning level with the school.
Class Levels:
- Basic Classes: These classes help students who need extra support.
- Regular Classes: These classes are designed for the average student.
- Advanced Classes: These classes are for students who want more challenging material. They might be called Honors, AP (Advanced Placement), or GTE (Gifted and Talented Education).
If you child has completed an i-Ready Placement Diagnostic test or a NWEA Map Test, you can refer to the charts at i-Ready Diagnostic Scores by Grade Level, and MAP Test Scores by Grade Level, for a better understanding of what the different scores mean.
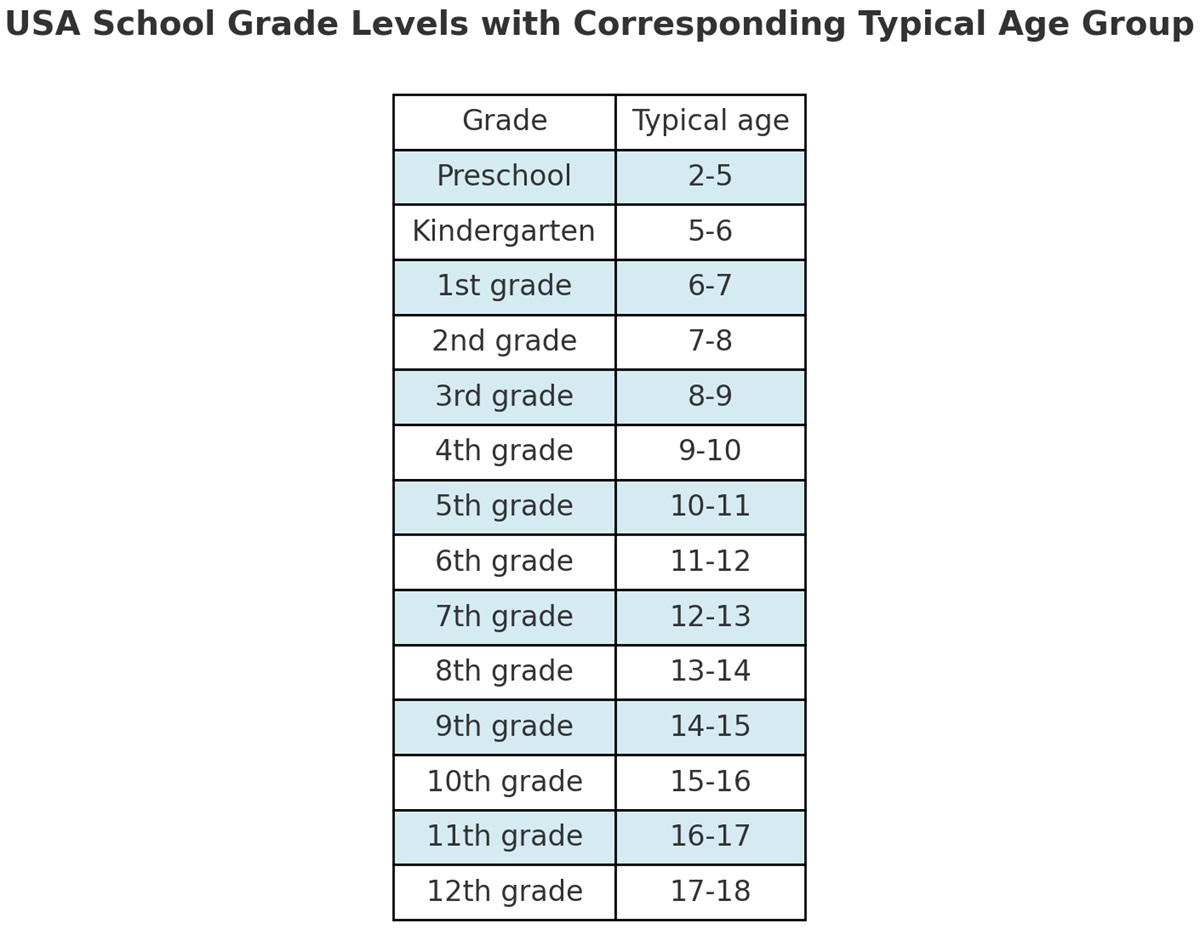
Elementary, Middle School and High School Grades System.
In the United States, the grade system is used to measure students’ academic performance throughout their educational journey. The U.S. grading system varies depending on the level of education (elementary, middle, high school, and college) and the institution, but the most common grading system uses letter grades to represent a student’s performance in each course. Here’s a breakdown of what the U.S. grade system looks like:
1. Letter Grades
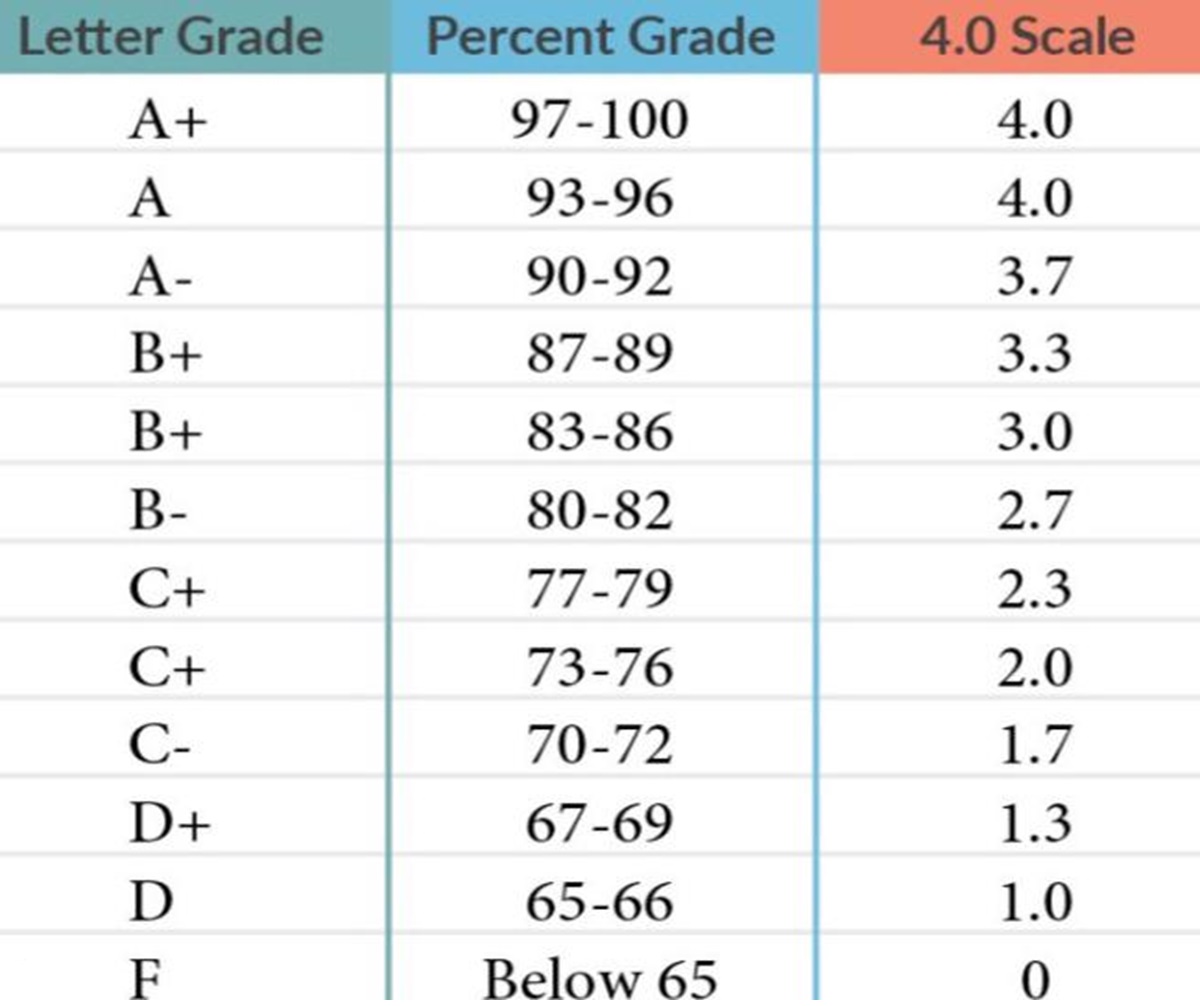
The most common way to represent grades in the U.S. is by using letter grades. Each letter grade typically corresponds to a range of percentage scores and has an equivalent Grade Point Average (GPA) value. Here’s what the letter grades generally represent:
- A (90-100%): Excellent – GPA Value: 4.0
- B (80-89%): Good – GPA Value: 3.0 to 3.9
- C (70-79%): Average – GPA Value: 2.0 to 2.9
- D (60-69%): Below Average – GPA Value: 1.0 to 1.9
- F (Below 60%): Fail – GPA Value: 0.0
These grades are given at the end of each semester or academic year and contribute to a student’s overall GPA.
2. Grade Point Average (GPA)
- GPA is a number that represents a student’s overall academic performance. It is calculated by averaging the GPA values of all the letter grades a student has earned.
- GPA Scale: The typical GPA scale is from 0.0 to 4.0, where 4.0 is the highest possible average. Some schools use a weighted GPA scale (e.g., up to 5.0 or even higher) to give additional points for honors, Advanced Placement (AP), or International Baccalaureate (IB) classes.
For example, a student who earns mostly A’s might have a 4.0 GPA, while a mix of A’s, B’s, and C’s could bring the GPA down to around 3.0 or lower.
3. Percentage Grades
In addition to letter grades, many teachers use percentage grades to reflect student performance on individual assignments, quizzes, tests, and projects. The percentage represents the score a student receives out of 100. For example:
- 95% to 100% usually translates to an A.
- 85% to 89% generally translates to a B.
4. Elementary and Middle School Grades
- In elementary (grades K-5) and middle school (grades 6-8), grading systems may vary from school to school.
- In addition to the letter grades, some elementary schools use descriptions like “Exceeds Expectations”, “Meets Expectations”, or “Needs Improvement” to evaluate younger students’ performance.
- Middle school often uses the same A-F grading system as high school.
5. High School Grading System
- High school (grades 9-12) uses letter grades and GPAs that play a major role in determining college admissions.
- Honors and AP/IB Classes: Students who take advanced classes like AP or IB courses may receive a weighted GPA, which means an A in an AP class could be worth 5.0 instead of 4.0, reflecting the difficulty level of the course.
What is a Passing grade in High School?
In high school in the United States, a passing grade is typically any grade D or higher. Here’s a breakdown:
- A (90-100%): Excellent
- B (80-89%): Good
- C (70-79%): Average
- D (60-69%): Below Average – Passing
- F (Below 60%): Fail – Not Passing
A D grade (usually 60-69%) is often considered the minimum requirement for passing a class. However, it’s important to note that different schools, states, or specific courses might have slightly different requirements for passing. Some classes may require a C (70%) or higher to be considered passing, especially if they are core classes needed for graduation.
6. College and University Grading System
- Letter Grades and GPA: College and university students receive letter grades and have a GPA that represents their cumulative academic performance. A student must usually maintain a minimum GPA to stay in good academic standing.
- Pass/Fail System: Some college courses may be graded on a Pass/Fail basis rather than using letter grades. In this system, students simply receive a Pass if they meet the minimum requirements or a Fail if they do not.
7. Weighted vs. Unweighted GPA
- Unweighted GPA: This GPA scale does not take the difficulty of courses into account. An A in an easy class and an A in an AP class both receive the same GPA value of 4.0.
- Weighted GPA: This GPA scale gives extra points for more challenging classes like honors or AP. For example, an A in an honors class might be worth 4.5, while an A in an AP class might be worth 5.0.
8. Grading Scales by Institution
- The grading scale may vary slightly between institutions, but the system of assigning letter grades from A to F remains standard.
- + and – Grades: Some schools use plus and minus grades to indicate slightly better or worse performance within each letter grade. For instance:
- B+ (87-89%): 3.3 GPA
- B- (80-82%): 2.7 GPA
U.S High School Grade System Conversion Chart.
Grade Level Placement for New Students in the USA.
When new students move to the United States, they must be placed in a grade level that best fits their educational needs. Placement may involve taking tests, to determine what grade is best for them. If a student’s placement doesn’t seem right, parents can discuss it with teachers or school administrators to better match their child’s abilities.
If a student doesn’t speak English well yet or has missed school due to difficult circumstances, such as being a refugee, schools may make adjustments to help them catch up.
These assessments help schools understand the student’s academic skills, English proficiency, and knowledge of core subjects to place them where they can learn most effectively. Below are the common types of placement tests foreign students may take in the U.S. education system:
1. English Language Proficiency Tests
For students whose first language is not English, schools often assess English proficiency to decide whether the student needs support in learning English. Common assessments include:
- WIDA ACCESS: This is an English proficiency assessment used to evaluate speaking, listening, reading, and writing skills. It helps determine if the student requires English as a Second Language (ESL) classes.
- English Language Proficiency Assessments for California (ELPAC): In California, this test is used to evaluate the English proficiency of students who are non-native speakers.
- Language Assessment Scales (LAS): This is another commonly used test for determining English language skills in students.
These tests help schools place the student in the appropriate English language development program to support their learning.
2. Mathematics Placement Tests
Mathematics skills can vary widely from country to country, so foreign students often take math placement tests to determine their current level of math knowledge. These tests generally include topics ranging from basic arithmetic to algebra, geometry, and more advanced mathematics.
- The purpose of these tests is to determine if the student needs additional support in math or if they are ready for grade-level or advanced classes.
- Schools might also use diagnostic tools like iReady to assess math skills.
3. General Knowledge Assessments
Schools may also use general assessments to evaluate a student’s knowledge in subjects like science, reading comprehension, and social studies. These assessments are used to see if the student is on par with the standards expected in U.S. schools. Some commonly used assessments include:
- NWEA MAP Growth Test: This is an adaptive assessment that evaluates math, reading, and language arts skills. The test adjusts in difficulty based on the student’s answers and helps determine the appropriate grade level and any areas needing additional support.
- Smarter Balanced or PARCC Assessments: In some states, foreign students may take state-specific standardized assessments to evaluate their proficiency in subjects like English and mathematics.
4. Diagnostic and Placement Tools
Some schools use diagnostic tools designed specifically to assess new students’ abilities across various subjects. Examples include:
- iReady Diagnostic: Used to assess reading and math skills for personalized learning plans.
- STAR Assessments: These are used to evaluate reading and math skills and provide a detailed profile of the student’s abilities.
5. Grade-Level Assessments
To determine the most appropriate grade level for a new student, schools may use:
- Basic Skill Tests: These tests assess the student’s understanding of core concepts like reading, writing, and math at different grade levels.
- Interviews and Written Assessments: Some schools might have students participate in interviews or write short essays to better understand their language abilities, interests, and academic background.
FAQ – U.S School Grade Levels.
We have added answers to the most commonly asked questions about the U.S education level system, below.
What grade is a 2 year old in?
A 2-year-old is typically in preschool or early childhood education. At this age, children may attend daycare or early learning centers, but they are not in a formal school grade yet.
What grade is a 3 year old in?
A 3-year-old is usually in preschool. They are not yet in kindergarten, but they may be attending a preschool program that focuses on socialization and early learning.
What grade is a 4 year old in?
A 4-year-old is typically still in preschool or may be in a pre-kindergarten (pre-K) program, which helps prepare them for kindergarten the following year.
What grade is a 5 year old in?
A 5-year-old is generally in kindergarten. This is the first formal year of school in the U.S. and focuses on basic literacy, math, and social skills.
What grade is a 6 year old in?
A 6-year-old is usually in 1st grade. This is the beginning of elementary school where students focus on reading, writing, math, and foundational subjects.
What grade is a 7 year old in?
A 7-year-old is typically in 2nd grade. They continue building on early literacy and numeracy skills.
What grade is an 8 year old in?
An 8-year-old is usually in 3rd grade. At this level, students continue to develop reading comprehension, math, and other core skills.
What grade is a 9 year old in?
A 9-year-old is typically in 4th grade. Students start learning more advanced topics in subjects like math, science, and social studies.
What grade is a 10 year old in?
A 10-year-old is generally in 5th grade. This is often the final year of elementary school, preparing students for middle school.
What grade is an 11 year old in?
An 11-year-old is usually in 6th grade. This is the beginning of middle school (or sometimes called junior high school).
What grade is a 12 year old in?
A 12-year-old is typically in 7th grade, which is in the middle of the middle school years.
What grade is a 13 year old in?
A 13-year-old is usually in 8th grade. This is often the last year of middle school, preparing students for high school.
What grade is a 14 year old in?
A 14-year-old is typically in 9th grade, also called Freshman year of high school.
What grade is a 15 year old in?
A 15-year-old is generally in 10th grade, known as Sophomore year of high school.
What grade is a 16 year old in?
A 16-year-old is usually in 11th grade, also called Junior year of high school.
What grade is a 17 year old in?
A 17-year-old is typically in 12th grade, known as Senior year of high school, which is the final year before graduation.
What grade is an 18 year old in?
An 18-year-old is generally still in 12th grade (Senior year), depending on their birthday and when they started school. Alternatively, they may have already graduated from high school.
These ages can vary slightly depending on the child’s birthday and school system policies, but this is a general guide to typical grade levels in the U.S. education system.
How old are you in preschool?
Children in preschool are usually 2 to 4 years old. Preschool focuses on early learning and socialization before starting kindergarten.
How old are you in pre-kindergarten (Pre-K)?
Children in pre-kindergarten (Pre-K) are typically 4 to 5 years old. This is a preparatory year before entering kindergarten.
How old are you in kindergarten (K)?
Children in kindergarten are generally 5 to 6 years old. This is the first formal year of school.
How old are you in 1st grade?
Children in 1st grade are typically 6 to 7 years old. This is the beginning of elementary school.
How old are you in 2nd grade?
Children in 2nd grade are usually 7 to 8 years old.
How old are you in 3rd grade?
Children in 3rd grade are generally 8 to 9 years old.
How old are you in 4th grade?
Children in 4th grade are typically 9 to 10 years old.
How old are you in 5th grade?
Children in 5th grade are usually 10 to 11 years old. This is often the last year of elementary school.
How old are you in 6th grade?
Children in 6th grade are generally 11 to 12 years old. This is the beginning of middle school or junior high.
How old are you in 7th grade?
Children in 7th grade are typically 12 to 13 years old.
How old are you in 8th grade?
Children in 8th grade are usually 13 to 14 years old. This is often the last year of middle school.
How old are you in 9th grade?
Students in 9th grade are generally 14 to 15 years old. This is the beginning of high school and is known as Freshman year.
How old are you in 10th grade?
Students in 10th grade are typically 15 to 16 years old. This year is called Sophomore year.
How old are you in 11th grade?
Students in 11th grade are usually 16 to 17 years old. This is known as Junior year.
How old are you in 12th grade?
Students in 12th grade are generally 17 to 18 years old. This is the final year of high school and is called Senior year.
These ages can vary slightly depending on the school district, a child’s birthday, or if a student skipped or repeated a grade, but this is the typical age range for each grade level in the U.S. education system.
How many credits to graduate High School?
In the U.S., the number of credits required to graduate from high school typically ranges from 18 to 24 credits, depending on the state and school district. These credits include core subjects such as English, math, science, and social studies, along with elective courses. Some states may have additional requirements, such as completing community service hours or passing specific exams.
What grade is Preschool?
Preschool is not part of the K-12 grade system; it is considered early childhood education for children aged 2 to 4 years old. It takes place before kindergarten and helps prepare children for formal schooling.
What grade is Elementary School?
Elementary School generally includes grades Kindergarten (K) through 5th grade. This usually means students are between the ages of 5 and 11.
What grade is Middle School?
Middle School includes grades 6th through 8th. Students in middle school are typically between the ages of 11 and 14.
What grade is High School?
High School includes grades 9th through 12th. Students are usually between the ages of 14 and 18 during high school.
How many years of education is mandatory in the U.S.?
In the U.S., education is mandatory for 12 years, generally from kindergarten (or age 5-6) to 12th grade (age 17-18). The exact age range can vary slightly from state to state, but children must attend school from roughly age 5 to 18.
Is Homeschooling legal in the U.S.?
Yes, homeschooling is legal in the United States. Parents have the right to educate their children at home, but homeschooling regulations and requirements vary by state. States may require things like submitting an intent to homeschool, following a specific curriculum, or participating in standardized testing.

hey, News Room, was wondering if u could clear something up for me. My kiddo is turning 4 soon and I’m looking at the part about what grade they’d be in. Would that mean pre-K or something else? Kinda new to all this school stuff. Thanks!
Hey Tammi, not News Room but my kid started pre-K at 4. Seems right.
TammiLou89, JakeS is correct. Children usually start Pre-K at 4. It’s a great way to introduce them to the school environment.
so about this GPA thing, hows it actually work? like, do all classes count the same or some more than others? kinda confused 🤔
Back in my day, we didn’t have all these fancy grading systems and we turned out just fine. What’s with the need to complicate everything?
Hey everyone, I just graduated and saw a lot of friends stress over GPA. It’s not just about how high ur GPA is but also the courses u take. Some are weighted more cause they’re harder. So, aim for a mix. Also, extracurriculars count a lot for college apps. Just my two cents.
I’m curious about how homeschooling fits into this? With so many grades and standardized systems, where do homeschoolers stand in terms of grades and age? Thanks for shedding light on this, News Room.